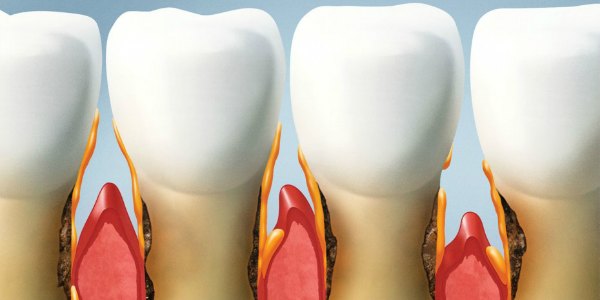
 It seems more and more types of cancer can be traced to gum disease! Read the research findings below and thank you for visiting Advanced Endodontics, Lakewood, Ohio!
It seems more and more types of cancer can be traced to gum disease! Read the research findings below and thank you for visiting Advanced Endodontics, Lakewood, Ohio!
University of Louisville School of Dentistry researchers have found a bacterial species responsible for gum disease, Porphyromonas gingivalis, is present in 61 percent of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The findings, published recently inInfectious Agents and Cancer, only detected P. gingivalis in 12 percent of tissues adjacent to the cancerous cells, while this organism was undetected in normal esophageal tissue.
“These findings provide the first direct evidence that P. gingivalis infection could be a novel risk factor for ESCC, and may also serve as a prognostic biomarker for this type of cancer,” said Huizhi Wang, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor of oral immunology and infectious diseases at the UofL School of Dentistry. “These data, if confirmed, indicate that eradication of a common oral pathogen may contribute to a reduction in the significant number of people suffering with ESCC.”
The esophagus, a muscular tube critical to the movement of food from the mouth to the stomach, is lined with two main kinds of cells, thus there are two main types of esophageal cancer: adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The latter is more common in developing countries.
In collaboration with the College of Clinical Medicine of Henan University of Science and Technology in Luoyang, China, Wang and his UofL colleagues Richard J. Lamont, Ph.D., Jan Potempa, Ph.D., D.Sc., and David A. Scott, Ph.D., tested tissue samples from 100 patients with ESCC and 30 normal controls.
Continue reading original content HERE: